Security researchers at WIZ have discovered a chain of vulnerabilities in NVIDIA’s Triton Inference Server that, when exploited together, could allow a remote, unauthenticated attacker to gain complete control of the server.
What’s Triton, anyway?
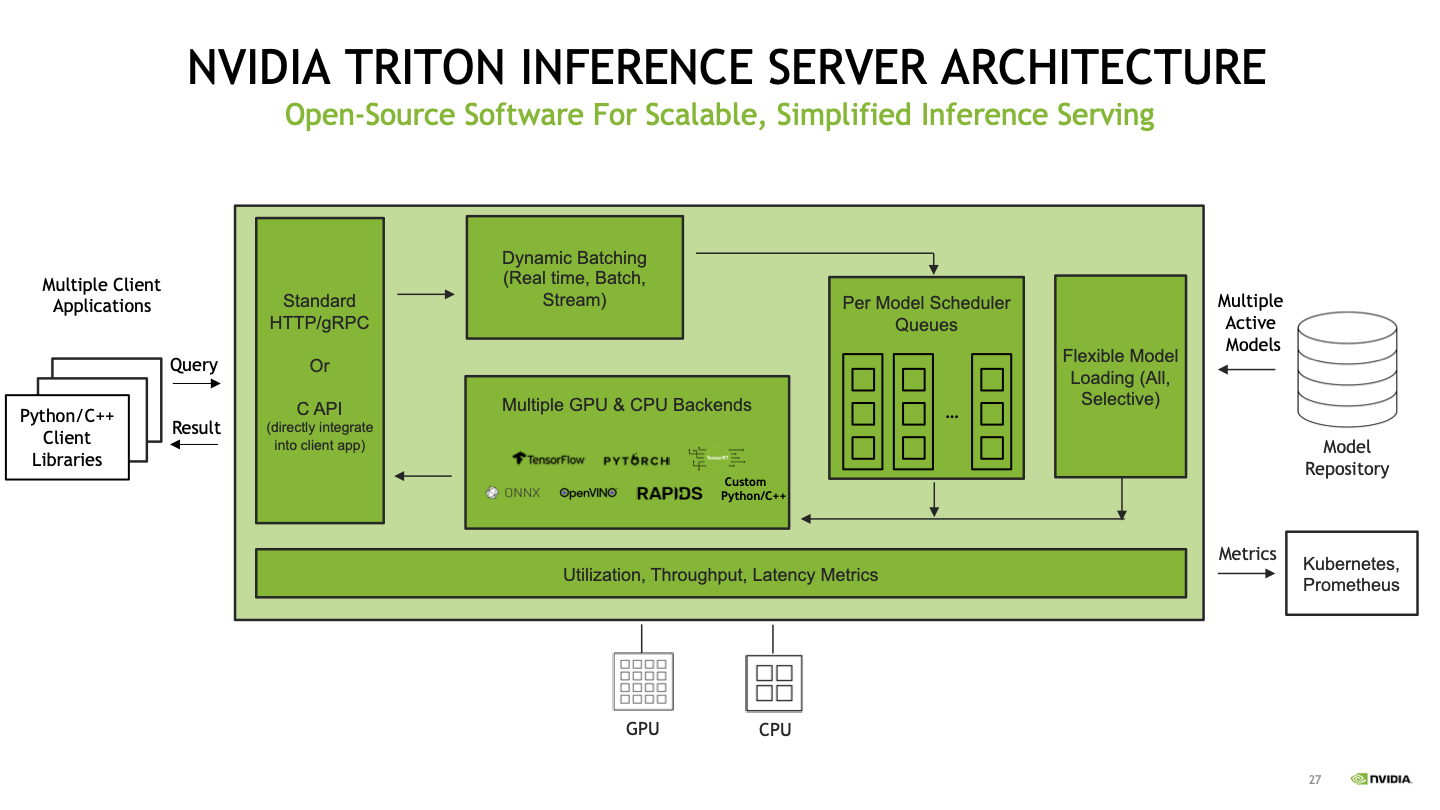
Triton is NVIDIA’s open-source inference server designed to make deploying AI models in production easier, faster, and more scalable.
It allows developers to serve models built in popular frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and ONNX, all through a unified API.
In practical terms, Triton acts like a high-performance gateway: you send it input data (like an image or a text prompt), and it runs the model and returns the result — often in real-time.
This process is typically accelerated by powerful GPUs, enabling fast and efficient inference, even under heavy workloads.
Because it’s optimized for serving AI at scale, Triton is widely used in industries like healthcare, finance, e-commerce, and autonomous vehicles — wherever real-time AI predictions are needed.
And guess what? All that power can now be hijacked.
The Vulnerabilities
Here’s a breakdown of the discovered issues:
- CVE-2025-23319 (CVSS score: 8.1): A vulnerability in the Python backend where an attacker could cause an out-of-bounds write by sending a specially crafted request.
- CVE-2025-23320 (CVSS score: 7.5): A flaw in the Python backend that allows an attacker to exceed the shared memory limit by sending an excessively large request.
- CVE-2025-23334 (CVSS score: 5.9): Another Python backend issue that enables an out-of-bounds read through crafted requests.
Each vulnerability on its own is dangerous. But chained together? That’s when things get really bad.
So, how does the attack work?
Here’s a simplified version of the attack:
- Use CVE-2025-23320 to trigger an error message that leaks the internal name of Triton’s shared memory region, something that should be kept private.
- With this leaked information, register your own access to that shared memory segment.
- Then, exploit the other vulnerabilities to read and write arbitrary data in the backend memory.
- Finally, inject your own code and hijack the server completely.
No login needed. No authentication required. Just straight-up remote code execution. This is every DevOps team’s nightmare.
Potential Impact
If successfully exploited, these vulnerabilities could lead to:
- AI Model Theft: Attackers gaining access to proprietary and costly AI models.
- Data Breach: Sensitive information processed by the models, such as personal or financial data, could be intercepted.
- Manipulated Outputs: Altering AI model responses to produce incorrect, biased, or malicious outputs.
- System Compromise: Using the hijacked server as a stepping stone to attack other systems within the organization’s network.
For a technical deep dive, check out the report written by WIZ’s security team:
Wiz Blog: NVIDIA Triton Vuln Chain